A 6 Step Plan for Trading Market Volatility
Trading market volatility can reap great rewards, and it doesn't have to be scary.
As long as you’re educated about your trade, and stay focused on managing risk, then you set yourself apart from the others. Let’s walk through some key steps for success.
- Step 1. Avoiding the #1 Option Trading Mistake
- Step 2. Most Important Option Factor
- Step 3. How Option Pricing Works
- Step 4. Knowing & Using the Market Maker’s Secrets
- Step 5. Highest Probability Option Strategies for Every Market
- Step 6. Risk-to-reward
Step 1. Avoiding the #1 Option Trading Mistake
All too often, options traders – especially new ones – will trade out of the money options simply because they cost less than long-dated options.
But is this the best approach?
Let’s say you’re bullish on Facebook (FB) at $100 a share. Some options traders may be tempted to buy a call option with 30 days remaining on the contract with a $120 strike.
The only reason they’re doing that is because the option is 15 cents, or $15 a contract and they can own a lot of them on the cheap. Now, though, they have to hope the stock itself can run from $100 to $120 prior to expiration.
If FB hits $121 in the next 30 days, sending the same call to $1.05, they made a killing.
That kind of leverage is incredible for them. But don’t do it.
The problem with this approach is they have to be right about the direction of the stock move, as well as the timing. That alone increases the odds against the trade working out.
To make any money at all, the stock must go well above the strike price in a set time frame. And the odds of a stock running from $100 to $120 that fast aren’t too good, unless there’s powerful news that could send it higher.
This dual objective of having to be right on direction plus on timing really lessens the probability of an option trade being a winning trade when buying options.
In order to make money on an Out-of-the-money call, you either need to outwit the market or get plain lucky. Being close means no cigar in the market unfortunately.
Based on this trade example, a better goal for every trader would be to select trades based on what provides the most consistent, positive returns, not a one-time big winner.
Where there’s a big disadvantage, such as the one you saw in the option buying scenario, you can usually just look at the flip side of the coin and see an equal and opposite advantage.
In this case, being a SELLER of options gives you a huge advantage over being a buyer of options. All of the pros know this and take advantage of it, and so can you. As a seller, all of the things in this example are the same, but in your favor, instead of against you.
This is why a lot of people take advantage of Selling Options for Profit Generation & Hedging.
But how is this done & what is involved?
Step 2. Most Important Option Factor
The most important option factor for income generation is the concept of TIME.
Time Value ~ is used for trading strategies that take advantage of the accelerated Time Decay of an option into its Expiration. Option Income Strategies are very tied to Time Value and the impact it has on the price of an option.
What exactly is Time Value?
- Time value (TV) (extrinsic) of an option is the premium a rational investor would pay over its current exercise value (intrinsic value), based on its potential to increase in value before expiring.
- This probability is always greater than zero, thus an option is always worth more than its current exercise value.
Take a look at the following chart to see just how predictable and powerful this option paradigm is! And answer the question that follows:
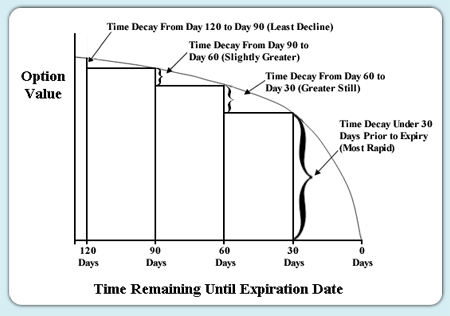
If the underlying security price was to go sideways, having no directional trend, would you have wanted pick an option 90 to 120 days out or would you have rather SOLD an option?
This is the common natural time value progression for all options.
Step 3. How Option Pricing Works
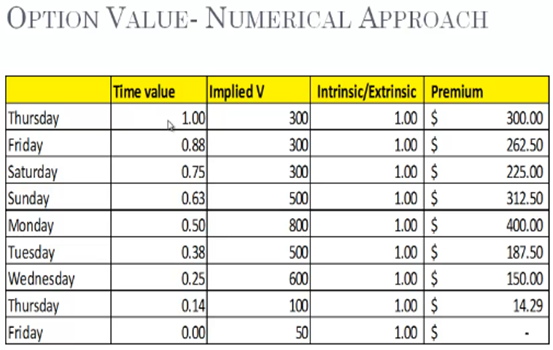
This is how you can value an option.
Time Value (x) Implied Volatility (x) Intrinsic/Extrinsic Value . . .
Note: Once you know these variables, then you are ready to price an option & know what its option premium should be.
Step 4. Knowing & Using the Market Maker’s Secrets
- Broad markets tend to have 2 to 3 week cycles and will trade in sideways channels 70% to 80% of the time.
- Based on this sideways price movement Out-of-the-money (OTM) option buyers will lose approximately 70% of the time.
- Market makers know these statistics and, therefore, tend to trade from the sell side.
- This is the professional money, so you need to think like a market maker.
- It’s all based on the Math!
- Market Makers use mathematical market probability statistics for pricing the movement of an option to its expiration.
- Knowing the probability of an underlying security finishing within a certain range at expiration is key when determining what options to buy or sell and what option strategies to implement.
- These statistics forecast how likely it is that an option will fall within a certain price, up or down, by its expiration.
- This statistical forecast is referred to as the Implied Move of the Stock.
- The Implied move is an estimate of a +/- standard deviation move of the underlying security by its expiration.
- Based on these probability statistics, Selling options & option spreads, when used correctly, provides the highest probability trade set-ups for generating consistent profits and is also a great way to hedge risk . . .
It’s all based on the math of probabilities.
GOOGL – Implied Move: +/- 4 Option Expiration 10 days
Trading Probabilities
Trading is a business of probabilities, and to be successful a trader needs to focus on controlling risk. One important step is to know the winning probabilities of any trade taken.
One simple & free tool for measuring probabilities is:
The Option Delta
- It will tell you the value of an option based on the underlying move.
- It is also used to measure the probability of a price move on the underlying move itself.
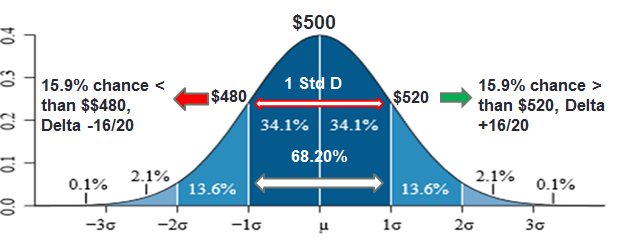
An Option Delta of 68/70 equates that the strike has a 68%/70% probability of being ITM at expiration.
An Option Delta of approximately +/- 16 is equivalent to the outside point of a 1 STD Implied move at expiration.
This equates that the 16 Delta strike has only a 16% theoretical probability of being ITM at expiration.
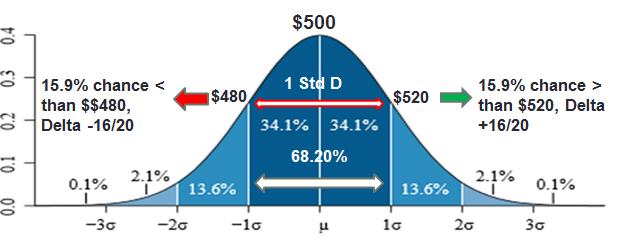
GOOGL: A 1 Standard Deviation Implied Move using the Think or Swim (TOS) Option Analyzer & showing the call option delta.
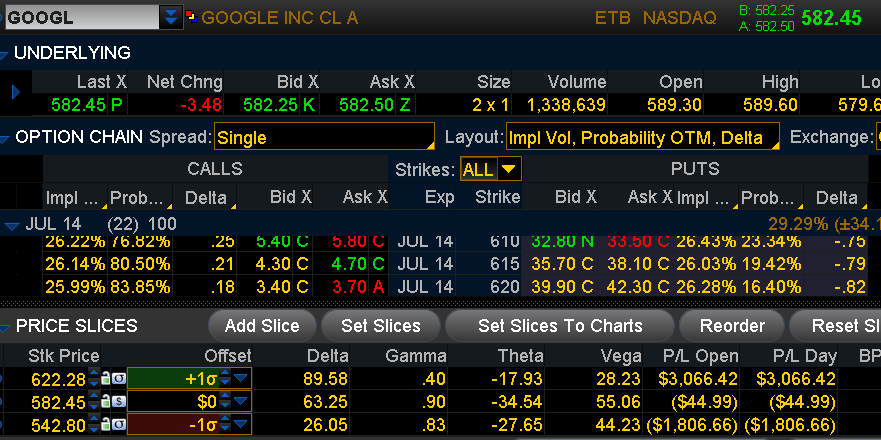
Using this probability analysis provides traders with a very useful tool for determining price targets to trade against and it’s also very useful for setting hedges.
Based on the math of probability, you can see that approximately 68.2% of options bought expire worthless, and, based on this, it’s a good idea for all traders or investors to consider selling options as well as simply buying them.
This added option strategy for profits and hedging will make a dramatic and positive difference in one’s trading performance when used correctly.
Step 5. Highest Probability Option Strategies for Every Market
The goal of every trader should be to select trades based on what provides the most consistent positive return and not always the greatest return. One of the best ways to achieve this is by knowing the income option strategies that are available and then selecting the one that is best for your trading style and trading plan.
Income Strategies
- Covered Calls
- Calendar Spreads
- Diagonal Spread
- Long Iron Condors
- Credit Spreads
Credit Spreads are often favored for four reasons:
- It can work regardless of market direction
- It almost always works even if you’re wrong!
- The winning probability of profit is over 68% even without adding technical analysis, which then increases the profit probability even more
- Perfect for hedging
There are 3 types of Credit Spreads:
- Bear Call Credit Spread
- Bull Put Credit Spread
- Long Iron Condor
Bear Call Credit Spread is best if you think the market is probably going to go down.
Strategy: Selling one call with a lower strike while simultaneously buying one call with a higher strike in the same month.
Selling a Bear Call Credit Spread → 25% Return on Margin
Credit Spread/Max Profit: $100/Ct. Return on Margin: $100/$400 = 25%
Bull Put Credit Spread is best when you think the market will probably go up
Strategy: Sell one put while simultaneously buying one put with a lower strike in the same month.
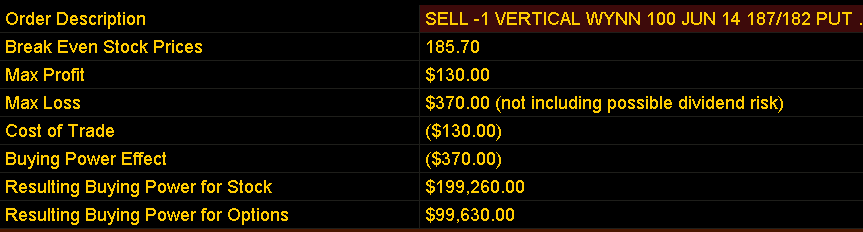
Selling Bull Put Credit Spread
Credit Spread/Max Profit: $130/Ct. Return on Margin: $130/$370 = 35%
Long Iron Condor – Known for being a non-directional, low-risk trading strategy
Strategy: Combine Bull Put Credit Spread and a Bear Call Credit Spread
Step 6. Risk-to-reward
2 Long Directional Options Strategies
Strategy 1. Buying Directional Calls
Strategy 2. Selling an Out-of-the-Money Bull Put Credit Spread
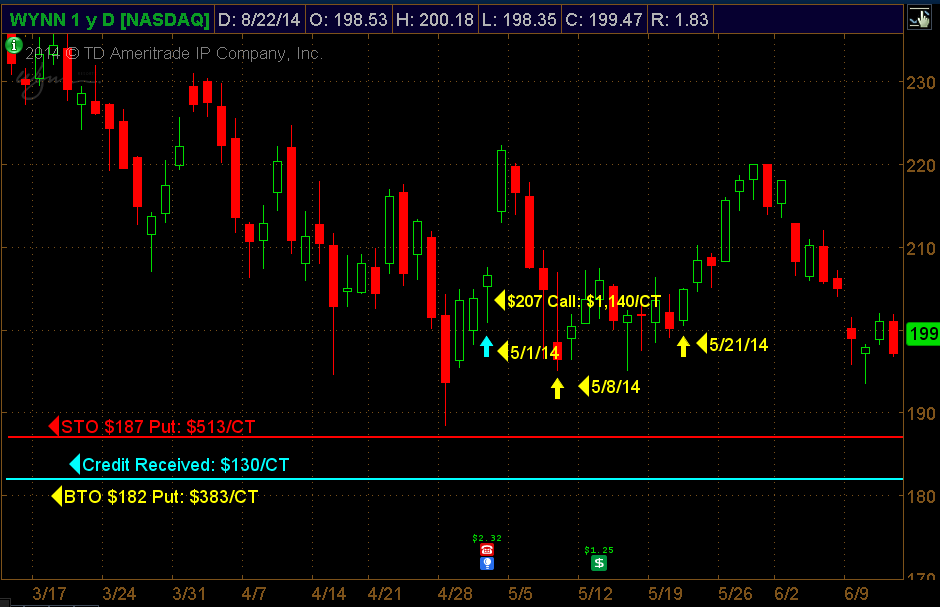
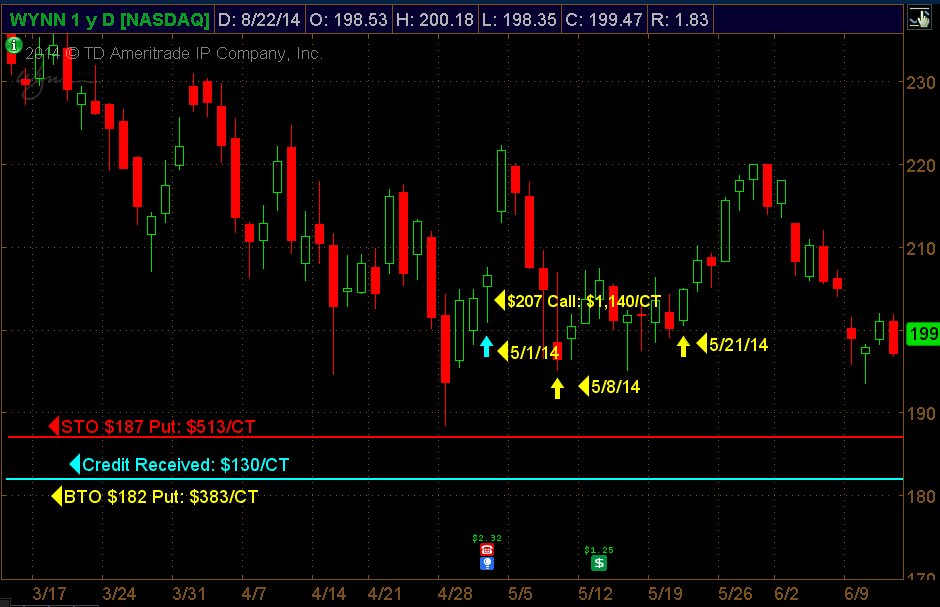
Wynn Resorts: Bullish Option Strategies
(1) Buying Directional Calls Vs (2) Selling Bull Put Credit Spread
Entry: May 1 Wynn Trading at $207
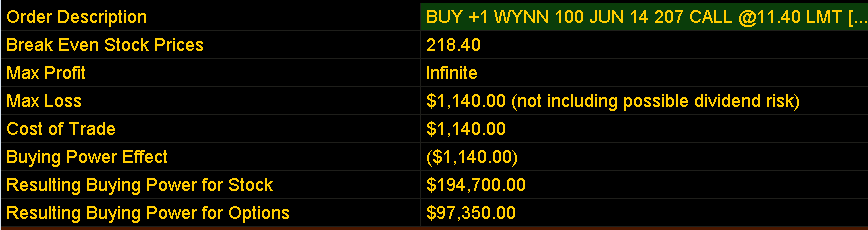
Strategy 1: Bought the ATM June $207 Call Strike for $11.40 or $1,140 per option contract
Strategy 2: Sold the $187/$182 OTM Bull Put Credit Spread. Spread sold below Wynn’s prior low of $189, which was 9.50% below its trading price of $207 on May 1st.
Strategy 1: Buying Long June $207 Calls
Entry: May 1
Trading at: $207
Debit & Capital at Risk: $1,140 per option contract
Return potential = Infinite
Open position P/L May 8
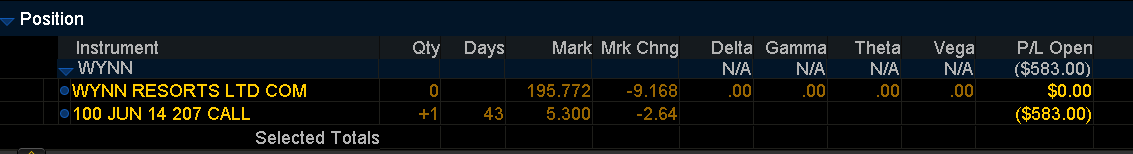
June Monthly $207 call original cost: $1,140 per option contract
WYNN trading at $196 P/L: - $583 per option CT.
Open position P/L May 21
June Monthly $207 call original cost: $1,140 per option contract
WYNN trading at $205 P/L: - $518 per option CT.
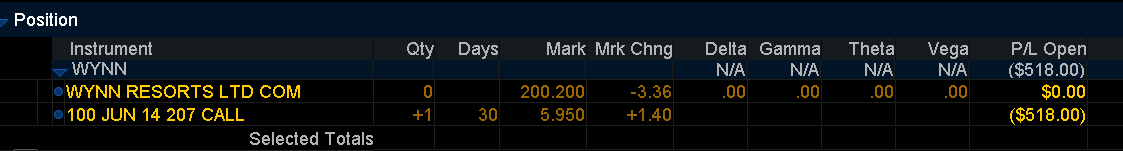
Strategy 2: Selling Bull Put Credit Spread
Entry: May 1
Trading at: $207
Credit Spread/Max Profit: $130/Ct. Return on Margin: $130/$370 = 35%
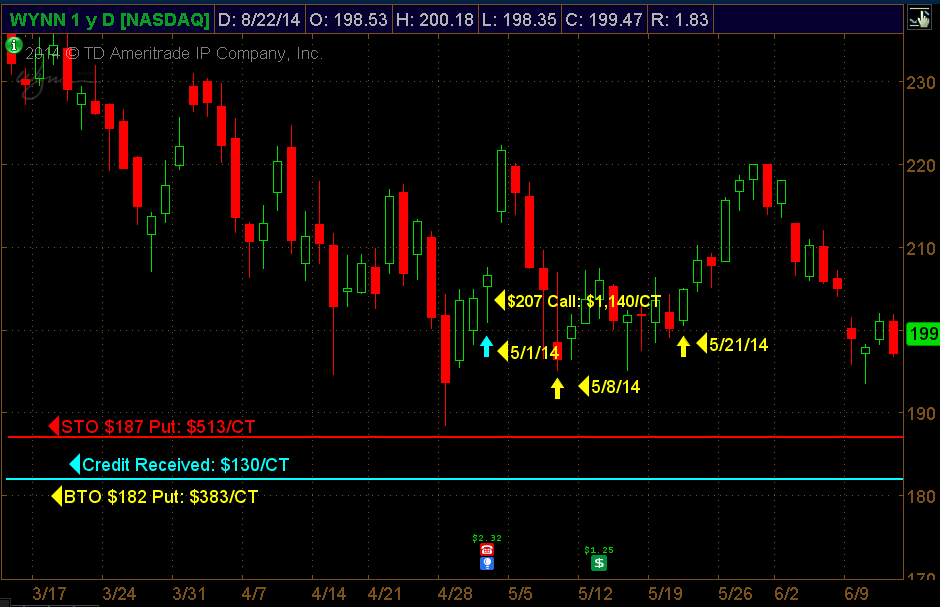
Strategy 2: June $187/$182 Bull Put Credit Spread: $130/Ct.
Open position P/L May 8:
WYNN trading at $196 Credit Spread: -$38.50/Ct. vs Long Call -$583
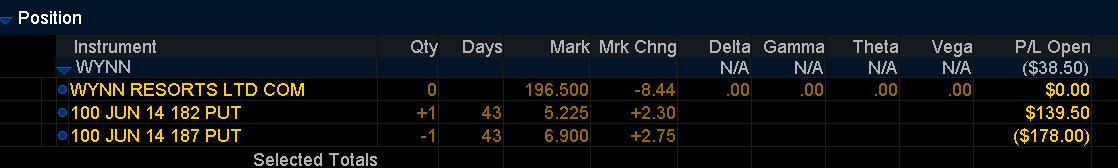
Strategy 2: June $187/$182 Bull Put Credit Spread: $130/Ct.
Open position P/L May 21
WYNN trading at $205 Credit Spread: $78.50/Ct. vs Long Call -$518/Ct.
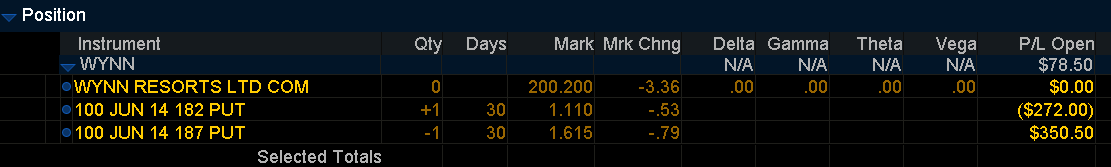
Based on these examples, which option strategy works best for you?
In the end, whether trading a small account or large account selling options and option spreads will have a major positive impact on your trading bottom line while reducing your trading risk.
These low-risk trading strategies offer income and profit while also providing the perfect hedging strategy. Any trader can easily execute these option strategies that can turn that small trading account into a large trading account and with much lower risk than the traditional buy only option strategy.



